To switch
To switch
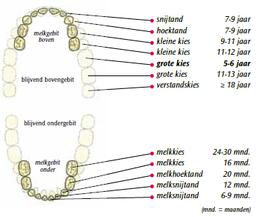
Permanent teeth replace milk teeth
Most children lose their teeth from the age of 6e year. The transition period is a very important phase in the development of permanent teeth. The breaking of the teeth and molars of the permanent teeth follows a certain pattern (see drawing). The permanent tooth or molar dissolves, as it were, the roots of the milk tooth or molar. This causes the milk tooth or molar to become loose and fall out. The permanent tooth or molar will replace it.
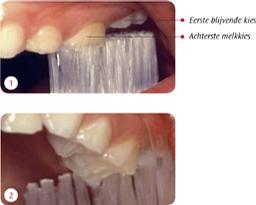
Many children and parents do not notice that the first permanent molars erupt. This usually happens before the front teeth change. They break through behind the last milk tooth. This makes them a bit hidden. Taking care of these molars is very important. The enamel of the newly erupted tooth is still very porous and fragile. Brush the tips of the new molars as soon as they come through.
Around 12e years, behind the first permanent molars, again permanent molars break through. They are also extra sensitive to getting cavities just after breaking through. Wisdom teeth are the last molars to erupt. Some people don't get wisdom teeth.
When new molars come through, the gums often swell. That is normal. It may hurt, but don't worry.
Differences between milk teeth and permanent teeth
The incisors of the permanent teeth have a serrated edge. Milk teeth don't have those. The serrated edge consists of three bumps on the cutting surface. The serration will disappear over time through natural wear.
Permanent teeth and molars have stronger enamel than milk teeth and molars. In addition to the white milk teeth, the permanent front teeth appear darker and/or yellower in color. This is normal. Brushing will not help to make them lighter in color.
Abnormalities in the development of children's teeth
In some cases, the development of the teeth is abnormal. Your dentist or dental hygienist will see this during the periodic check-up. He will take measures in consultation. The following abnormal developments require advice from your practitioner:
- Your child is almost eight years old and has not yet changed.
- There are more than six months between changing a tooth on the left and right jaws.
- A new tooth or molar comes through, but the milk tooth or molar is still stuck. The new tooth or molar then appears in front of or behind the baby tooth or molar.
- Your son or daughter is in pain for a longer time than his peers.
Please note: good oral hygiene remains necessary, even if brushing your teeth hurts.
Temporary crooked teeth in children's teeth
The teeth of the permanent teeth can break through slightly crooked. Sometimes many teeth erupt at once. Then it seems as if 'too many' teeth have come into that little mouth. That is not a problem, because the jaw will continue to grow for a while. Then there will be more room for the permanent teeth. Often, the position of the teeth will eventually settle itself.
Care when changing
thumb sucking
Many toddlers suck on their thumb, teat or finger. Some children squeeze their tongue against the palate when swallowing, pressing it between the upper and lower teeth. Thumb, finger or teat sucking and tongue pressing affect the position of the teeth. Try to stop your child from sucking and tongue pressing. Do this before erupting the permanent front teeth. For example, hand over something or distract your child during the day. Or reward your child if they have stopped for a certain amount of time. Can't get rid of bad habits? Ask your dentist or dental hygienist for advice.
Brushing and brushing in children
Usually, children want to brush their teeth themselves at a young age. That's fine. Please encourage that. They just don't do this equally well everywhere. Brush the teeth of children until they are 10 years old at least once a day, even if your child uses an electric brush. Older children can usually brush independently. Even then it does not hurt if you check occasionally whether the teeth are clean. For example, use dental plaque detectors. This is a red dye in tablet form that makes dental plaque visible. You can buy the tablets at the drugstore. Does (after) brushing cause problems? Ask your dentist or dental hygienist for advice.
Pay attention to the following when (after) brushing:
- Brush the teeth of children from 5 years 2x a day with fluoride toothpaste for adults. You can also use toothpaste marked "child" or "junior." Then look at the age indicated here (for example 5-12 years).
- Use a special brush for the children's mouth. Choose a variant with soft bristles and a small brush head. Don't press too hard. Replace the brush if the bristles are no longer aligned. As soon as children can hold a toothbrush, they can also brush electrically. Electric brushing is not better for children, but some children cooperate better if you use an electric toothbrush.
- Brush at least once a day, even if your child uses an electric brush.
- Make sure you have a good view in the mouth and that there is sufficient support for your child's head when you brush (after). Try out which brushing position is most comfortable for you. For example, stand diagonally behind your child. If you support the chin with your hand, the head rests
against your upper body. Bend over your child a little so you can see where you are brushing. Or stand in front of your child and let him rest his head against the wall, for example. Support the chin with one hand while you brush with the other. This way you can clearly see where you are brushing. - When brushing, pay extra attention to the breakthrough
rear molars. Place the brush across the row of teeth here. - Does your child wear braces that cannot be removed? Then pay extra attention to (after) brushing. Plaque easily remains between the braces and the teeth. Ask your dentist or dental hygienist how best to brush and re-brush.
- Will the gums bleed despite good brushing technique? Then consult your dentist or dental hygienist. Your child may need additional resources.

Eating and drinking and children's teeth
In addition to brushing well, brushing afterwards and checking by the dentist or dental hygienist, it is important that you pay close attention to your child's nutrition. Plaque forms on and between the teeth: a barely visible, sticky white-yellow layer. The bacteria in the dental plaque convert sugars (for example from candy, cake, soft drinks and fruit) and starch (for example from potatoes, pasta, bread or crackers) in the mouth into acids. Those acids cause cavities (caries) in the teeth. Soft drinks, fruit (juice) and, for example, sports drinks contain acids as well as sugars. These acids can dissolve tooth enamel. This form of wear is called dental erosion. To prevent cavities and dental erosion, limit the number of eating and drinking moments to a maximum of 7 per day: 3x a meal and a maximum of 4x a snack. Encourage your child to drink tap water.
Treatments during the transition in children
Holes in the milk teeth
The most common problem with primary teeth is cavities, also known as caries. They usually start in the molars. Cavities can be prevented by careful brushing of your teeth and a sensible diet. You can also stop starting holes and prevent a hole from getting bigger. The dentist or dental hygienist will give appropriate advice about nutrition and brushing your teeth. Cavities that do enlarge can cause pain or inflammation. This can also cause damage to the permanent teeth. Sometimes the dentist or dental hygienist has to remove the caries (drill) and fill the tooth. He is happy to explain to you and your son or daughter why he chooses which approach.
It is important for several reasons that a hole (caries) in a milk molar or tooth does not get bigger:
- A hole can lead to pain and inflammation.
- The milk molar still has to function for a while to keep space free for the molar of the permanent teeth.
- An inflammation in the milk teeth can affect the permanent teeth.
sealing
Molars have many grooves on the chewing surface. Plaque forms easily in it. Plaque not removed regularly can cause cavities. So brush well! If the dentist or dental hygienist sees a hole forming in the chewing surface, he may decide to apply a layer. This is called sealing. He can seal deep grooves by sealing. Only the permanent molars are normally eligible for sealing. This usually happens shortly after they break through completely. You also need to brush sealed molars well.
Extra fluoride
If cavities threaten to appear, the dentist can advise extra fluoride use. For example, he can advise you to brush your teeth extra or use a fluoride mouthwash. The dentist can also decide to apply extra fluoride himself, using a brush or spoon. Brushing your teeth remains the basis of dental care.
What to do in case of an accident?
An accident can cause a tooth to fall out or be damaged. In such situations, contact your dentist immediately. Find all loose pieces or the complete tooth as soon as possible and take it to the dentist. Never put back a fallen baby tooth. This can damage the new permanent tooth. Keep a lost tooth or chipped tooth moistpreferably with milk. Preferably do not rinse the tooth under the tap. No milk within reach? Then keep the tooth or part of the tooth loose in the mouth of the parent/carer, preferably in the space between the molars and the cheek.