Inflamed gums
Inflamed gums
Prevent inflamed gums through good oral hygiene
Good oral hygiene keeps your teeth, molars and gums healthy. This prevents inflamed gums (gingivitis and periodontitis) and promotes their healing. But how do you know if your gums are healthy? And can you recognize inflamed gums?
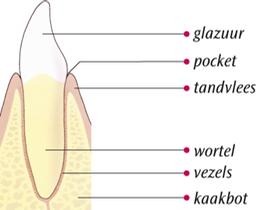
Healthy gums
Healthy gums are pink, fit tightly around teeth and do not bleed when you eat or brush your teeth. Healthy gums are the basis of healthy teeth. The gums, together with the jawbone and the fibers, are the foundation of your teeth. If you keep your gums healthy, you can enjoy your own teeth for years to come.
Inflamed gums (gingivitis)
Bleeding, red or swollen gums usually indicate inflamed gums. Your gums may be inflamed anywhere. But the inflammation can also be local, for example between 2 teeth. Inflamed gums are sometimes accompanied by a bad taste in the mouth or bad breath. It rarely hurts, but the gums can be sensitive to the touch. You will notice this when you brush your teeth, use toothpicks, interdental brushes or dental floss. Sometimes your gums are inflamed, but nothing is visible. Fortunately, your dental hygienist or dentist can diagnose the inflammation. Timely treatment of inflamed gums can preserve your teeth.
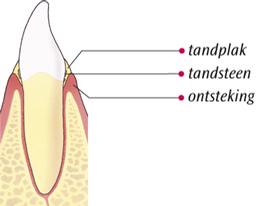
What Causes Inflamed Gums?
Plaque on the transition from your gums to your tooth and the plaque that is between your teeth cause inflamed gums. If you don't remove plaque properly, the bacteria in the plaque will cause your gums to become inflamed. Dental plaque that is not removed can harden and calcify into tartar. New plaque easily adheres to tartar. This causes the gums to become increasingly inflamed. Dental plaque is difficult to see. A dental plaque detector is a handy tool to make dental plaque visible.

Severe gingivitis (periodontitis)
The inflammation of the gums can spread to the jaw bone. The inflammation causes the gums to detach from the teeth. The space (pocket) between the tooth and the gums becomes deeper. The inflammation in the gum line can spread to the jaw bone. This causes the gums to loosen even further. The inflammation causes the fibers to break and the jawbone to break down. Consequence? Even deeper pockets. In this, the dental plaque partially calcifies into tartar. The gums may recede. This progressive inflammation with breakdown of fibers and jaw bone is called periodontitis. You often do not feel periodontitis and can do without a good one
control go unnoticed for a long time.
Periodontitis is often not noticed until the teeth loosen or if the space between the teeth becomes loose
teeth and molars become larger. Because the gums have receded far, roots are exposed.
Exposed roots have no protective glaze. This makes holes easily. Teeth and molars with exposed roots are also sensitive. For example, when you brush your teeth or when you eat or drink hot, cold, sweet or sour products. The inflammation can cause so much jawbone to disappear that your teeth and molars fall out.
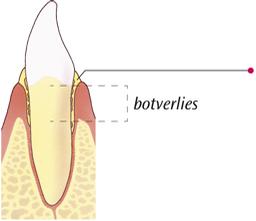
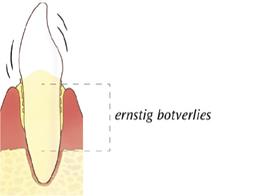
How do you know if the inflammation is serious?
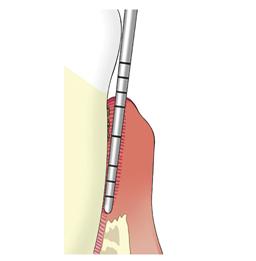
On the eye, all the inflamed gums look the same. To determine the severity of an infection, the dentist or dental hygienist must measure the spaces between the teeth and gums (pockets). He does this with a so-called pocket probe on all teeth. With the measurement, he determines the severity of the inflammation per tooth. In healthy gums, a pocket is a maximum of 3 mm and does not bleed. Inflamed gums give pockets up to 5 mm. More advanced inflammations have even deeper pockets, often 6mm or even more. Then there is also bone breakdown.
What should I do to make and keep my gums healthy?
Inflamed gums only heal if you remove all plaque on a daily basis.
My gums are inflamed, how do I remove all the plaque?
With good oral hygiene you remove all dental plaque. That means more than brushing your teeth for 2 minutes twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. Also clean the spaces between your teeth daily with toothpicks, brushes or dental floss. Good daily oral hygiene is the basis of healthy gums and a healthy mouth.

What can the dentist do about inflamed gums?
Your dentist or dental hygienist can advise you and give you instructions on how to improve and maintain your oral hygiene. With good oral hygiene you remove dental plaque from your teeth every day in the places where you can reach yourself with a toothbrush, toothpicks, interdental brushes or dental floss. You cannot brush away tartar yourself. Your dental care provider does this with special instruments. This is called dental cleaning. Your daily efforts together with professional dental cleaning in the oral care practice will be rewarded. The inflammation can disappear and healthy gums can reattach to the teeth. The gums may recede slightly during healing. Jawbone once lost will not come back. Whoever removes all dental plaque daily prevents new infections.
Can I remove plaque with a mouthwash?
Some mouthwashes make plaque removal easier. However, they cannot replace the use of a toothbrush combined with toothpicks, interdental brushes or dental floss. Mouthwashes can give a fresh mouth odor and pleasant taste.
Is smoking harmful to my gums?
In addition to the known health risks, smoking also has adverse effects on your gums. The gums of smokers appear paler and bleed less easily, while they may still be inflamed. If you smoke, the gums recover worse from inflammation. In smokers, the jaw bone breaks down 2x faster than normal.
I am pregnant. Am I more likely to get inflamed gums?
You are more likely to get gum problems during your pregnancy. Due to the changed activity of your hormones, the gums react more violently to the presence of dental plaque. Extra attention to oral hygiene during your pregnancy is therefore very important. If you carefully remove all plaque, your pregnancy will not put you at extra risk of gum disease.
Does stress affect gum disease?
Everyone suffers from stress from time to time. Prolonged psychological stress can suppress the body's defenses and therefore also the gums. Those who are under a lot of stress have a greater chance of periodontal disease. The consequences of periodontitis can also be more serious.
Does diabetes affect my gums?
Someone with diabetes is more susceptible to inflammation and infection. So also the gums inflame faster. This happens especially when the diabetes is not properly controlled. People with diabetes, and especially diabetes that is not properly controlled, have an increased risk of developing periodontitis.